.NET SDK
Amica.net
The Amica.net SDK allows a C#, F#, or VB developer to leverage our APIs with no need to write custom code to talk with them. It has been designed and carefully hand-crafted by our engineering team and it is used in production by our Amica Web Application and several other tools.
The code is open-source and developed in public on GitHub. The package is available on Nuget.
Keep your package updated
As our APIs evolve, so do our SDK, so make sure to frequently check Nuget for packages updates.
Installation
Installling the SDK is as simple as adding an Amica.net package reference to your project.
dotnet add package amica.net --version 1.0.0
NuGet\Install-Package amica.net -Version 1.0.0
<PackageReference Include="amica.net" Version="1.0.0" />
If you use Visual Studio, JetBrains' Rider, or any other IDE, you may use your favorite IDE's UI to achieve the same goal. On this page, we use CLI examples as they are valid on any platform and are more concisely showcased.
Tutorial
We want to write a small app from scratch.
Our goals are:
- Create a new .NET project;
- Install Amica.net as a project dependency;
- Set both API Key and Application ID;
- Log in with a valid user (autenticate);
- Download the list of companies available to the user;
- Obtain some company's client/vendor records.
In this tutorial We will be using VS Code, but you can follow along with any editor or IDE of choice.
Create a new .NET project
In your terminal, start a new console project named Amica.net.Tutorial:
dotnet new console -o amica-dotnet-tutorial -n Amica.net.Tutorial
Then, cd into the newly created directory:
cd amica-dotnet-tutorial
Install the Amica.net package
Make sure you are in the amica-dotnet-tutorial directory, then type the follwoing command:
dotnet add package amica.net
Now, launch VSCode from within the current directory:
code .
The above command will open VSCode on the current project:
Tip
We assume that the VSCode C# Dev Kit is already installed. If not, please install it before continuing.
Set the API key and the App ID
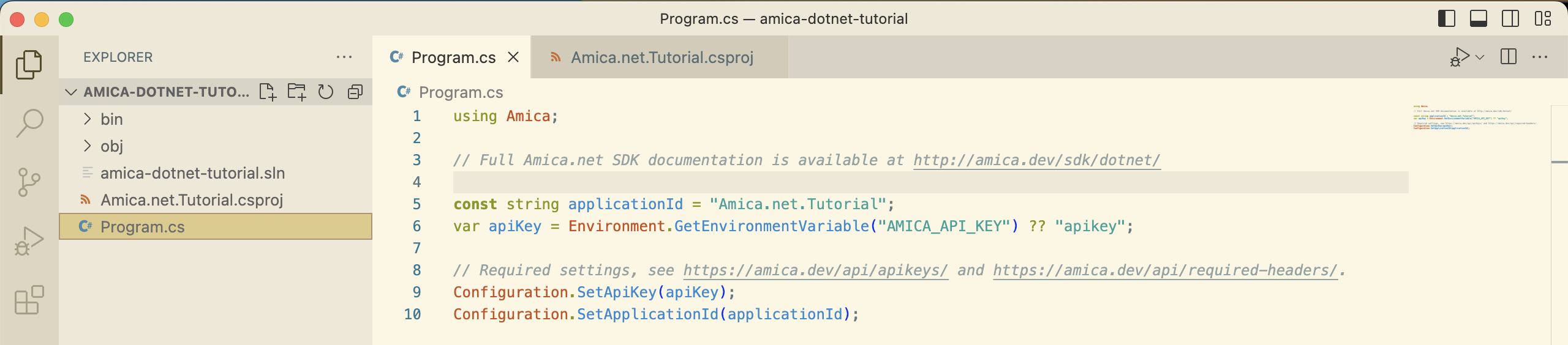
Now, delete all the code in Program.cs and replace it with the following lines:
using Amica;
const string applicationId = "Amica.net.Tutorial";
var apiKey = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AMICA_API_KEY") ?? "apikey";
Configuration.SetApiKey(apiKey);
Configuration.SetApplicationId(applicationId);
Imports Amica
Const applicationId = "Amica.net.Tutorial"
Dim apiKey as String = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AMICA_API_KEY") or "apikey"
Configuration.SetApiKey(apiKey)
Configuration.SetApplicationId(applicationId)
As the API key is sensible information, we retrieve it from an environment variable. This way, its value won't be checked in in version control or appear anywhere in the codebase.
Tip
Setting environment variable values is a task achieved differently based on the operating system and IDE or editor you are using, which goes beyond this tutorial's scope. For VSCode, maybe check the answers to this Stack Overflow question.
Setting the Application ID is straightforward.
The Configuration class exposes some properties and methods such as
SetApiKey and SetApplicationId that allow, you guessed it, proper SDK
configuration. As the API key and the Application ID are required for most
API requests, we set them immediately.
In VSCode, our code should now look like this (click to enlarge):
Now, hit F5 on the keyboard to launch the app and select "C#" as the debugger. The program should be built and then run, but nothing happens. That's OK; we only wanted to verify Amica.net is appropriately installed and configured.
Log in a user (authenticate)
Most API endpoints require an authentication token. This token is obtained by
authenticating as a valid user. A user is authenticated by logging in with the
user's credentials. Add the following code to the Program.cs file:
var userName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AMICA_USER") ?? "user";
var password = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AMICA_PASSWORD") ?? "password";
var (loginResult, token) = await SessionManager.Login(userName, password);
if (!loginResult.IsSuccess)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Login failed ({loginResult.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})");
return;
}
Dim userName as String = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AMICA_USER") or "user"
Dim password as String = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AMICA_PASSWORD") or "password"
Dim loginResult = Await SessionManager.Login(userName, password)
If Not loginResult.response.IsSuccess Then
Console.WriteLine($"Login failed ({loginResult.response.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})")
Return
End If
Again, as the username and password are sensible information, we retrieve them from the environment.
The SessionManager.Login method allows us to validate user credentials and
obtain the authentication token we'll use for all our requests on behalf of the
user. Notice that the method returns a tuple. The first value is of
Response<LoginResult> type, while the second is a nullable string that
contains the authentication token we're interested in. If login fails, we report
the failure and exit.
Tip
Most responses return a Response<T> or Response<List<T>> class instance. Response exposes several valuable properties, such as IsSuccess above or HttpResponseMessage that exposes the .NET HttpResponseMessage class instance for the request.
Once a token has been acquired, you can start working with the various API endpoints. In this tutorial, we will first obtain the list of companies (Azienda) available to the user, and then we'll download some clients and vendors from the first company on the list.
Download the companies' list
This SDK comprises several service classes, each dedicated to one API endpoint. Each service works with one particular data entity.
Since we now want to download the companies (Azienda) list, we must create an instance of the AziendaService class. Add the following line to Program.cs:
var aziendaService = new AziendaService();
Dim aziendaService As New AziendaService()
Once our service instance runs, we can invoke its List method to achieve our goal.
var requestSettings = new RequestSettings
{
TokenAuthentication = new() { Token = token! },
BaseAddress = loginResult.Result!.BaseAddress
};
var aziendaResponse = await aziendaService.List(settings: requestSettings);
if (!aziendaResponse.IsSuccess)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Companies 'List' request failed ({aziendaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine($"Available companies for user '{userName}:");
var companies = aziendaResponse.Result;
foreach (var company in companies!)
Console.WriteLine(company.Nome, company.LicenseKey);
Dim requestSettings As New RequestSettings With {
.TokenAuthentication = New TokenAuthentication With { .Token = loginResult.token },
.BaseAddress = loginResult.response.Result.BaseAddress
}
Dim aziendaResponse = Await aziendaService.List(settings := requestSettings)
If not aziendaResponse.IsSuccess Then
Console.WriteLine($"Companies 'List' request failed ({aziendaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})")
Return
End If
Console.WriteLine($"Available companies for user '{userName}:")
Dim companies = aziendaResponse.Result
for Each company in companies
Console.WriteLine(company.Nome, company.LicenseKey)
Next
Configuration.RequestSettings.TokenAuthentication = new() { Token = token! };
Configuration.RequestSettings.BaseAddress = loginResult.Result!.BaseAddress;
var aziendaResponse = await aziendaService.List();
if (!aziendaResponse.IsSuccess)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Companies 'List' request failed ({aziendaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine($"Available companies for user '{userName}:");
var companies = aziendaResponse.Result;
foreach (var company in companies!)
Console.WriteLine(company.Nome, company.LicenseKey);
Configuration.RequestSettings.TokenAuthentication = New TokenAuthentication With { .Token = loginResult.token }
Configuration.RequestSettings..BaseAddress = loginResult.response.Result.BaseAddress
Dim aziendaResponse = Await aziendaService.List()
If not aziendaResponse.IsSuccess Then
Console.WriteLine($"Companies 'List' request failed ({aziendaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})")
Return
End If
Console.WriteLine($"Available companies for user '{userName}:")
Dim companies = aziendaResponse.Result
for Each company in companies
Console.WriteLine(company.Nome, company.LicenseKey)
Next
Thread-safe vs. thread-unsafe
Notice that we have two different code snippets: thread-safe and thread-unsafe.
In the thread-safe code snippet, we pass a RequestSettings instance to the
List method. RequestSettings allows us to pass important information, such
as the authentication token and the base address (BaseAddress) returned by the
SessionManager.Login call we performed above. This approach requires us to
pass a RequestSettings instance on every method call but has the advantage
that calls can be concurrently executed.
In the thread-unsafe snippet, we don't pass a RequestSettings instance to the
method call but rather set the equivalent static properties of the
Configuration class. The List call is straightforward, and, more
importantly, we set the token and base address once, and then we forget about
it. The thread-unsafe approach can be used when performing single-thread
(non-concurrent) API calls.
When the request is successful, the response's Result property always contains
the requested items. If unsuccessful, Result will be null.
Always test for success
It is always a good idea to test whether a request has been successful by
checking the Response.IsSuccess property. In case of failure, you can
inspect Response.HttpResponseMessage and Response.ProblemDetails for
hints on what went wrong.
Get a Anagrafiche list
Now, we can pick one company (the first in the list) and request a list of some
of its clients. In this case, we leverage the AnagraficheService, responsible
for working with Anagrafica entities.
Add the following code to Program.cs:
var targetCompany = companies[0];
requestSettings.CompanyId = targetCompany.Id;
requestSettings.TokenAuthentication.LicenseKey = targetCompany.LicenseKey;
Console.WriteLine($"Retrieving the first ten clients of company '{targetCompany.Nome}'...");
var service = new AnagraficaService();
var options = new ListOptions<Anagrafica> { Take = 50 };
options.AddFilter(x => x.Cliente, Operator.EqualTo, true);
options.AddSort(x => x.RagioneSociale1, Direction.Descending);
var anagraficaResponse = await service.List(options, settings: requestSettings);
if (!anagraficaResponse.IsSuccess)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Anagrafiche 'List' request failed ({anagraficaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})");
return;
}
foreach (var anagrafica in anagraficaResponse.Result!)
Console.WriteLine(anagrafica.RagioneSociale1);
Dim targetCompany = companies(0)
requestSettings.CompanyId = targetCompany.Id
requestSettings.TokenAuthentication.LicenseKey = targetCompany.LicenseKey
Console.WriteLine($"Retrieving the first ten clients of company '{targetCompany.Nome}'...")
Dim service = New AnagraficaService()
Dim options = new ListOptions(Of Anagrafica) With{ .Take = 50 }
options.AddFilter(Function(x) x.RagioneSociale1, [Operator].EqualTo, true)
options.AddSort(Function(x) x.RagioneSociale1, Direction.Descending)
Dim anagraficaResponse = await service.List(options, settings:= requestSettings)
if (!anagraficaResponse.IsSuccess) Then
Console.WriteLine($"Anagrafiche 'List' request failed ({anagraficaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})")
Return
End If
For Each anagrafica in anagraficaResponse.Result
Console.WriteLine(anagrafica.RagioneSociale1)
Next
var targetCompany = companies[0];
Configuration.RequestSettings.CompanyId = targetCompany.Id;
Configuration.RequestSettings.TokenAuthentication.LicenseKey = targetCompany.LicenseKey;
Console.WriteLine($"Retrieving the first ten clients of company '{targetCompany.Nome}'...");
var service = new AnagraficaService();
var options = new ListOptions<Anagrafica> { Take = 50 };
options.AddFilter(x => x.Cliente, Operator.EqualTo, true);
options.AddSort(x => x.RagioneSociale1, Direction.Descending);
var anagraficaResponse = await service.List(options);
if (!anagraficaResponse.IsSuccess)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Anagrafiche 'List' request failed ({anagraficaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})");
return;
}
foreach (var anagrafica in anagraficaResponse.Result!)
Console.WriteLine(anagrafica.RagioneSociale1);
Dim targetCompany = companies(0)
Configuration.RequestSettings.CompanyId = targetCompany.Id
Configuration.RequestSettings.TokenAuthentication.LicenseKey = targetCompany.LicenseKey
Console.WriteLine($"Retrieving the first ten clients of company '{targetCompany.Nome}'...")
Dim service = New AnagraficaService()
Dim options = new ListOptions(Of Anagrafica) With{ .Take = 50 }
options.AddFilter(Function(x) x.RagioneSociale1, [Operator].EqualTo, true)
options.AddSort(Function(x) x.RagioneSociale1, Direction.Descending)
Dim anagraficaResponse = await service.List(options, settings:= requestSettings)
if Not anagraficaResponse.IsSuccess Then
Console.WriteLine($"Anagrafiche 'List' request failed ({anagraficaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})")
Return
End If
For Each anagrafica in anagraficaResponse.Result
Console.WriteLine(anagrafica.RagioneSociale1)
Next
When we work with company data, we must set the RequestSettings.CompanyId and RequestSettings.TokenAuthentication.LicenseKey values.
What is a license key?
Every company has an associated license key you or your client received upon
purchasing an Amica license. The license key is generally emailed a few
minutes after the purchase on our website. The Azienda.LicenseKey
property holds the company's license key.
Because we only want to download the first fifty records, we use the
ListOptions.Take option on invoking the List method. Combined with the
Skip option, Take allows us to perform data pagination as needed.
ListOptions has other exciting features, such as Expand for expanding
sub-objects, FilterBy for searches, and OrderBy for sorting. In the code
above, we add one filter (records must have the Cliente (client) flag set to
true) and sort by RagioneSociale1 descending. You can have multiple filters
and sortings.
If our request is successful, we cycle through the resultset and print each
company name (Anagrafica.RagioneSociale1) to the console.
Update a record
We want to add a note (Anagrafica.Note) to the first record. Add the following to Program.cs:
var client = anagraficaResponse.Result![0];
client.Note = "this is a note";
var resp = await service.Update(client, requestSettings);
if (!resp.IsSuccess)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Update failed ({anagraficaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Update success!");
Console.WriteLine("Exiting now...");
Dim client = anagraficaResponse.Result(0)
client.Note = "this is a note"
Dim resp = Await service.Update(client, requestSettings)
if Not resp.IsSuccess Then
Console.WriteLine($"Update failed ({anagraficaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})")
Return
End If
Console.WriteLine("Update success!")
Console.WriteLine("Exiting now...")
var client = anagraficaResponse.Result![0];
client.Note = "this is a note";
var resp = await service.Update(client);
if (!resp.IsSuccess)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Update failed ({anagraficaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Update success!");
Console.WriteLine("Exiting now...");
Dim client = anagraficaResponse.Result(0)
client.Note = "this is a note"
Dim resp = Await service.Update(client)
if Not resp.IsSuccess Then
Console.WriteLine($"Update failed ({anagraficaResponse.HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode})")
Return
End If
Console.WriteLine("Update success!")
Console.WriteLine("Exiting now...")
Wrapping up
We learned to correctly set up Amica.net and use API endpoints in read and write
operations. We learned that multiple service classes exist in the SDK,
approximately one per every API endpoint (or entity), and we can use those
instances to interact with the remote API. We didn't use all the service
methods, but the remaining ones (Add, Delete, Get) are used similarly to
the ones seen above. There are other utility classes and services in the SDK,
but those are out of the scope of a getting-started tutorial.
You understand the .NET SDK design, are confident enough to use Amica.net and can start using it to consume Amica APIs.
API Reference
The complete .NET SDK API reference is available here.